Unobstructed primary mirror
The off-axis secondary mirror never blocks the incoming beam. More light, more contrast, less glare.
HONU is a compact, off-axis reflecting telescope inspired by the Hawaiian sea turtle. Its mirrors are arranged so that no hardware sits in the way of the incoming light, delivering clean, high-contrast views for visual observers and imagers alike.
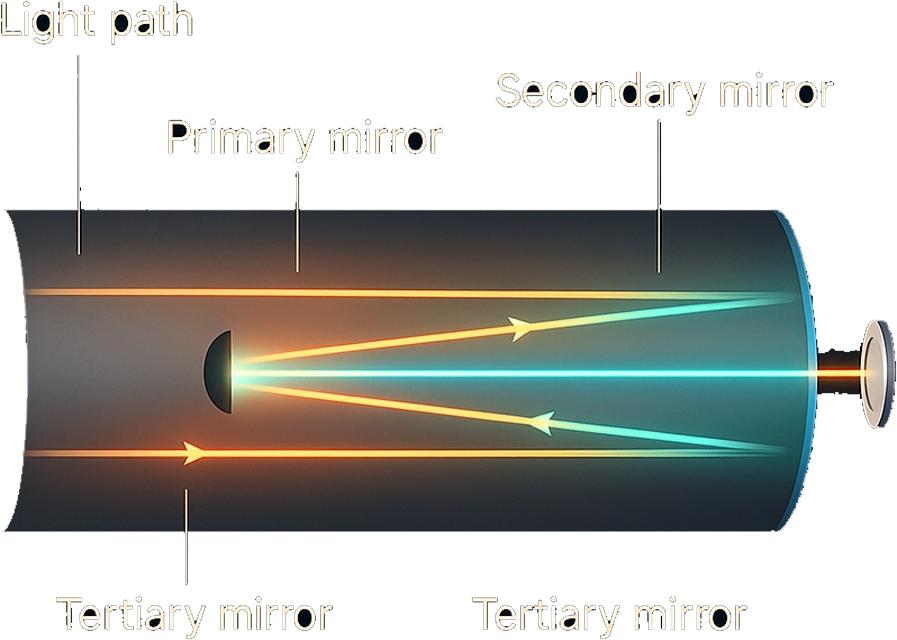
Explore how the HONU telescope uses mirrors to create an obstruction-free optical path. Each mirror plays a specific role in shaping a sharp, low-glare image.
Most modern reflecting telescopes place a secondary mirror directly in the incoming beam. The support structures for this mirror — often called spider vanes — slice through the light path and create visible diffraction spikes. Bright stars appear like crosses, and faint structures lose contrast.
HONU eliminates this problem completely. Its secondary mirror is positioned off-axis, so the full surface of the primary mirror can collect starlight without obstruction. The result is a cleaner, higher-contrast image with noticeably more detail in nebulae, galaxies and star clusters.
To guide the light to a convenient viewing position, HONU uses a dedicated tertiary mirror. This creates a compact, ergonomic layout — ideal for both visual observing and astrophotography — while preserving an unobstructed optical path.
Engineering such a design requires research-grade precision. Mirror shaping, alignment and calibration must be far more exact than in typical consumer telescopes. With MorphOptic technology, HONU brings this high-end optical performance into a portable telescope you can take anywhere.
The off-axis secondary mirror never blocks the incoming beam. More light, more contrast, less glare.
No spider vanes in the light path means no diffraction spikes — bright stars stay tight and round in your images.
A dedicated tertiary mirror guides the beam comfortably to your eye or camera, keeping the telescope compact and easy to balance.
Precision shaping and alignment techniques drawn from research telescopes, now applied to a portable instrument you can actually own.